What is TRICHOMONIASIS
Source:
http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/s...homoniasis.htm
Source:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002307/
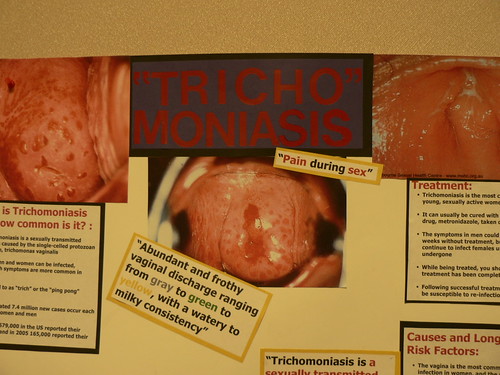
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis.
Trichomoniasis is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD) that affects both women and men, although symptoms are more common in women.
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
Trichomoniasis is found worldwide. In the United States, the highest number of cases are seen in women between age 16 and 35. Trichomonas vaginalis is spread through sexual contact with an infected partner. This include penis-to-vagina intercourse or vulva-to-vulva contact. The parasite cannot survive in the mouth or rectum.
The disease can affect both men and women, but the symptoms differ between the two groups. The infection usually does not cause symptoms in men and goes away on its own in a few weeks.
Symptoms
Women:
Discomfort with intercourse
Itching of the inner thighs
Vaginal discharge (thin, greenish-yellow, frothy or foamy)
Vaginal itching
Vulvar itching or swelling of the labia
Vaginal odor (foul or strong smell)
Men:
Burning after urination or ejaculation
Itching of urethra
Slight discharge from urethra
Occasionally, some men with trichomoniasis may develop prostatitis or epididymitis from the infection.
Signs and tests
In women:
A pelvic examination shows red blotches on the vaginal wall or cervix. A wet prep (microscopic examination of discharge) shows the infection-causing organisms in vaginal fluids. A pap smear may also diagnose the condition.
In men:
The disease can be hard to diagnose in men. Men are treated if the infection is diagnosed in any of their sexual partners. Men may also be treated if they have ongoing symptoms of urethral burning or itching despite treatment for gonorrhea and chlamydia.
Treatment
The antibiotic metronidazole is commonly used to cure the infection. A newer drug, called Tinidazole may be used.
You should not drink alcohol while taking the medicine and for 48 hours afterwards. Doing so can cause severe nausea, abdominal pain, and vomiting.
Avoid sexual intercourse until treatment has been completed. Sexual partners should be treated at the same time, even if they have no symptoms.
Expectations (prognosis)
With proper treatment, the outcome is likely to be excellent.
Complications
Long-term infection may cause changes in the tissue on the cervix. These changes may be seen on a routine Pap smear. In such cases, treatment should be started and the Pap smear repeated 3 to 6 months later.
Treatment of trichomoniasis helps prevents the spread of the disease to sexual partners. Trichomoniasis is common among persons with HIV.
Prevention
A monogamous sexual relationship with a known healthy partner can help reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections, including trichomoniasis.
Other than total abstinence, condoms remain the best and most reliable protection against sexually transmitted infections. Condoms must be used consistently and correctly to be effective.
How does trichomoniasis affect a pregnant woman and her baby?
Pregnant women with trichomoniasis may have babies who are born early or with low birth weight (low birth weight is less than 5.5 pounds).